Understanding the Passport PKI Trust Chain
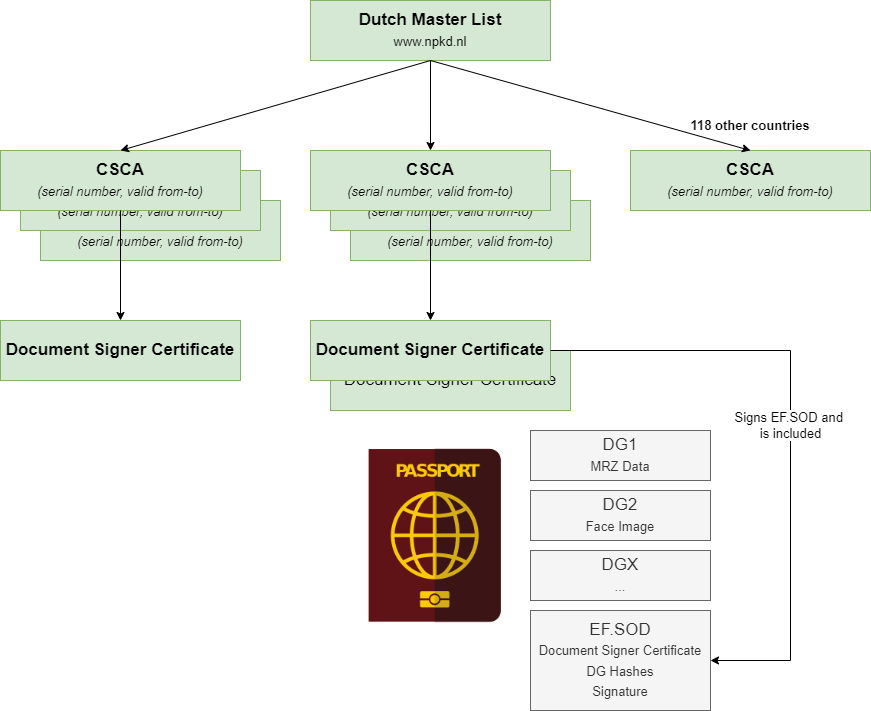
PKI Components Overview
In the context of electronic Machine Readable Travel Documents (eMRTDs), the trust model is built on a PKI similar to that used in web certificates, but governed under ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization) guidelines:
- CSCA (Country Signing Certificate Authority): Each country has one or more CSCAs which issue Document Signer Certificates (DSCs).
- DSC (Document Signer Certificate): Used to sign the EF.SOD, which contains hashes of data groups (e.g. face image, fingerprint).
- EF.SOD (Elementary File - Security Object Document): A signed object holding hashes of ePassport content.
The trust chain is:
EF.SOD ↔ signed by → DSC ↔ issued by → CSCA
To validate the EF.SOD:
- Extract the DSC from the EF.SOD.
- Match the DSC against the CSCA using the Masterlist.
- Confirm the signature is valid and the hash digest matches the ePassport content.
Masterlist and Trust Issues
The Masterlist is a file signed by a national authority (e.g., Netherlands), aggregating CSCAs from many countries. While the ICAO recommends this, trust issues arise because not all countries (e.g., USA) participate in signing or trusting others' masterlists.
Start by downloading:
- Masterlist.mls – contains ~394 CSCA certificates. (https://www.npkd.nl/index.html)
- Dutch Self-signed CSCA certificate.
- Dutch Link certificate (bridges certificate generations).
Step-by-Step Validation Using OpenSSL
Step-by-Step Validation Using OpenSSL
Step 1: Read EF.SOD and Inspect ASN.1 Structure
final hex = mrtdData.sod!.toBytes().hex();
Save hex to a file:
echo [hexstring] > sod.txt
xxd -r -p sod.txt > EF.SOD
Parse ASN.1 structure:
openssl asn1parse -in EF.SOD -inform DER -i
You will see something like:
0:d=0 hl=4 l=2659 cons: appl [ 23 ]
4:d=1 hl=4 l=2655 cons: SEQUENCE
OpenSSL cannot parse [APPLICATION 23], so skip the first 4 bytes:
dd if=EF.SOD of=EF.SOD.cms bs=1 skip=4
Step 2: Extract Document Signer Certificate (DSC)
openssl cms -inform DER -in EF.SOD.cms -verify -noverify -out /dev/null -certsout dsc.pem
Inspect it:
openssl x509 -in dsc.pem -text -noout
Convert to binary format:
openssl x509 -in dsc.pem -outform DER -out dsc.cer
Step 3: Unpack the Masterlist and Find the Matching CSCA
Download the Masterlist and associated Dutch certificates.
Use icao-ml-tools to parse the .mls:
python3 ml_to_csca_list.py MasterList.mls output_dir/
Get DSC's Issuer Serial Number from:
openssl asn1parse -in EF.SOD -inform DER -i
Find the corresponding CSCA in the unpacked masterlist (look for the matching serial or subject).
Convert CSCA file (usually .der) to .cer:
openssl x509 -in input.der -inform DER -out csca.cer -outform PEM
Step 4: Validate the DSC with the CSCA
Check if the CSCA signed the DSC:
openssl verify -CAfile csca.cer dsc.pem
Expected output:
dsc.pem: OK
Step 5: Extract and Inspect the Signed Content
This content contains hash values for each data group (DG1, DG2, etc.):
openssl cms -inform DER -in EF.SOD.cms -verify -noverify -out lds_content.der
To inspect:
openssl asn1parse -in lds_content.der -inform DER -i
You’ll see a structure with:
- DigestAlgorithmIdentifier
- DataGroupHashes
Step 6: Final Signature Verification of EF.SOD
Once you trust the CSCA, verify the full EF.SOD CMS signature:
openssl cms -inform DER -in EF.SOD.cms -CAfile csca.cer -out /dev/null -verify
Expected output:
CMS Verification successful